Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / Organisms G57321FI
G57321FI
Summary
- GlyTouCan ID
-
G57321FI
- IUPAC Condensed
- GalNAc(a1-
- Motifs
- Tn antigen
External Links
3D Structures
- GlycoNAVI
- G57321FI
- GLYCAM
- DGalpNAca1-OH
Organisms
| Organisms | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Armadillo | |
| Human immunodeficiency virus | |
| Escherichia coli | |
| Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) | |
| Toxocara canis (dog roundworm) |
Taxonomic Hierarchy
root
cellular organisms [inference]
Eukaryota (eucaryotes) [inference]
Opisthokonta [inference]
Metazoa (metazoans) [inference]
GlycoGene Database (GGDB)
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1GALT1 | (not applicable) |
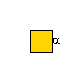 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
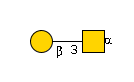 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
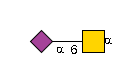 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
O-glycan Synthesis | |
| B3GNT6 | UDP-GlcNAc |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[alpha]-pNP |
 G00035MO
G00035MO
|
[alpha]-pNP |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1GALT1 | (not applicable) |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[Ala-Thr(*)-Ala]2-7 |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
[Ala-Thr(*)-Ala]2-7 | |
| ST6GALNAC4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
benzyl |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
benzyl | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST6GAL1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
para-nitrophenol | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
para-nitrophenol | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
benzyl | |
| ST8SIA6 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
KEGG BRITE Database
Core Protein
| UniProt ID | Protein Name | Reference | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q15517 | Corneodesmosin | ||
| Q15582 | Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 | ||
| Q15847 | Adipogenesis regulatory factor | ||
| Q15904 | V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 | ||
| Q16270 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 | ||
| Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 | ||
| Q16706 | Alpha-mannosidase 2 | ||
| Q16787 | Laminin subunit alpha-3 | ||
| Q16790 | Carbonic anhydrase 9 | ||
| Q2KHR3 | Glutamine and serine-rich protein 1 |
GlycoEpitope
- Epitope ID
- EP0021
- Epitope Name
- Tn Antigen
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| Ficolins bind to repetitive carbohydrate structures on the target cell surface | Mus musculus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Canis familiaris |
| Initial triggering of complement | Sus scrofa |
| Initial triggering of complement | Xenopus tropicalis |
| Initial triggering of complement | Homo sapiens |
| Initial triggering of complement | Gallus gallus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Bos taurus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Rattus norvegicus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Mus musculus |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Homo sapiens |
Sequence Descriptors
- GlycoCT
-
RES 1b:a-dgal-HEX-1:5 2s:n-acetyl LIN 1:1d(2+1)2n
- WURCS
- WURCS=2.0/1,1,0/[a2112h-1a_1-5_2*NCC/3=O]/1/
Literature (from GlyTouCan)
- BCSDB
-
- GlycoEpitope
-
 G00041MO
G00041MO
